从渲染集合到模块学习
使用 VS Code 可以安装 React 的代码片段 Snippets,安装在这里 。
善用 console.log 来进行调试,使用 console.log('props value is', props),用 , 分隔而不是用 + 连接 object。
在应用崩溃使用 console.log 来调试时,应该从最先渲染的组件开始插入 console.log 来排查出错问题的位置,然后结合 打印数组、对象等方式找出具体的问题并解决,直到程序正常运行为止。
JavaScript Arrays JS数组
学习视频,待整理
Rendering collections with Map method 用 Map 方法渲染集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
const notes = [
{
id : 1 ,
content : '我喜欢 react' ,
date : '2020-10-29T15:17:10.098Z' ,
important : true
},
{
id : 2 ,
content : '启动电脑开VS,欢迎来到编程世界。' ,
date : '2020-10-29T15:18:26.092Z' ,
important : false
},
{
id : 3 ,
content : 'GET 和 POST 是 HTTP 协议中最重要的方法' ,
important : true
}
]
const App = ( props ) =>
{
const { notes } = props
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< ul >
< li >{ notes [ 0 ]. content }</ li >
< li >{ notes [ 1 ]. content }</ li >
< li >{ notes [ 2 ]. content }</ li >
</ ul >
</ div >
)
}
ReactDOM . render (
< App notes = { notes } />,
document . getElementById ( 'root' )
)
以上 notes 数组仅有三个对象,可以通过引用一个硬编码的索引号 来访问数组中对象。
使用 map 函数从数组对象生成 React 元素。
1
notes . map ( note => < li >{ note . content }</ li >)
通过这样的方法可以生成 li 元素的数组。
1
2
3
4
5
[
< li > 我喜欢 react </ li >,
< li > 启动电脑开VS , 欢迎来到编程世界 。 </ li >,
< li > GET 和 POST 是 HTTP 协议中最重要的方法 </ li >,
]
现在重构之前的代码,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
const App = ( props ) =>
{
const { notes } = props
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< ul >
{ notes . map (
note => < li >{ note . content }</ li >
)}
</ ul >
</ div >
)
}
map 的工作方式
1
2
const result = notes . map ( note => note . id )
console . log ( result ) // 打印出 [1,2,3]
使用 map 方法会创建一个新数组,其元素是从原始数组通过 mapping 映射创建的,映射的逻辑是使用作为 map 方法传递进去的函数。
这个函数是
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
// 紧凑形式
note => note . id
// 以上函数的完整形式
( note ) =>
{
return note . id
}
该函数获取一个 note 对象作为参数,然后番位其 id 字段的值。
Key attribute Key属性
正如 React 列表 & Key 的说明,列表项,即 map 方法生成的每个元素 ,都必须有一个唯一的键值,名为 key 的属性。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
const App = ( props ) =>
{
const { notes } = props
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< ul >
{ notes . map ( note =>
< li key = { note . id }>
{ note . content }
</ li >
)}
</ ul >
</ div >
)
}
虽然说可以使用数组的索引作为键,避免控制台报错,但这仍然可能会导致意想不到的问题。 ,这有问题案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// 不要这样做
< ul >
{ notes . map (( note , index ) =>
< li key = { index }>
{ note . content }
</ li >
)}
Refactoring modules 重构模块
将 App 重构,使得 App 更简洁易用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// 新增 Note 组件
const Note = ({ note }) =>
{
return (
< li >{ note . content }</ li >
)
}
const App = ({ notes }) =>
{
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< ul >
{ notes . map ( note =>
< Note key = { note . id } note = { note } />
)}
< ul >
</ div >
)
}
此处要注意,这样必须在 Note 组件定义 key 属性,而不是在 li 标签定义。
通常来说,在较小型的应用中,组件一般放在 src/components 目录下,一般约定按照组件名称来命名文件。
例如创建一个 Node 组件,我们将 Node.js 文件存在 components 目录下,其文件内容为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import React from 'react'
const Note = ({ note }) =>
{
return (
< li >{ note . content }</ li >
)
}
export default Note
最后一行 export 是在声明模块,即变量 Note。
那么在使用这个组件的文件中,使用 import 方法来使用这个模块。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
import React from 'react'
import ReactDom from 'react-dom'
import Note from './components/Note'
const App = ({ notes }) =>
{
// ...
}
导入自己的组件时,它们的位置必须给出导入文件的相对路径。 './components/Note'
开头的 . 是指当前工作目录,因此引入文件的位置是当前目录下的 components 文件夹中的 Node.js 文件,其中 .js 可以省略。
表单
使用 useState 方法将新增的笔记添加到 App 组件状态中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
const App = ({ notes }) =>
{
const [ notes , setNotes ] = useState ( notes )
const [ newNote , setNewNote ] = useState ( 'a new note...' )
const addNote = ( event ) =>
{
event . preventDefault () // 阻止事件的默认操作
const noteObject =
{
id : notes . length + 1 ,
content : newNote ,
date : new Date (). toISOString (),
important : Math . random () < 0.5 ,
}
setNotes ( notes . concat ( noteObject )) // 使用 concat 方法来新建
setNewNote ( '' )
}
const handleNoteChange = ( event ) => setNewNote ( event . target . value )
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< ul >
{ notes . map ( note =>
< Note key = { note . id } note = { note } />
)}
< ul >
< form onSubmit = { addNote }>
< input value = { newNote } onChange = { handleNoteChange } />
< button type = "submit" > save </ button >
</ form >
</ div >
)
}
其中注意点 <input /> 组件中,如果只有 value={newNote} 属性受控,将会导致 input 组件渲染成一个只读元素,这将正确的修改 input 的value,必须搭配 onChange={handleNoteChange} 才能正确控制 input 元素的状态。相反的,如果只有 onChange={handleNoteChange} 而没有 value={newNote},那样 setNewNote('') 将不会重置 input 元素的值。
Filtering Displayed Elements 过滤显示的元素
三目运算符 - condition ? val1 : val2
当 condition 为 true 时,返回 val1,否则返回 val2
数组的 filter 方法 - arr.filter()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
import React , { useState } from 'react'
import Note from './components/Note'
const App = ( props ) => {
const [ notes , setNotes ] = useState ( props . notes )
const [ newNote , setNewNote ] = useState ( '' )
const [ showAll , setShowAll ] = useState ( true )
// ...
const notesToShow = showAll
? notes
: notes . filter ( note => note . important ) // 因为 note.important 本身是布尔值,所以省略了 '=== true' 的判断
return (
< div >
< h1 > Notes </ h1 >
< div >
< button onClick = {() => setShowAll ( ! showAll )}>
show { showAll ? '显示重要' : '显示全部' }
</ button >
</ div >
< ul >
{ notesToShow . map ( note =>
< Note key = { note . id } note = { note } />
)}
</ ul >
// ...
</ div >
)
}
通过三目运算符判断 showAll 的状态来过滤需要显示的数据以及按钮的值。
从服务器获取数据
一般的项目包含前端「客户端」和后端「服务端」。截至目前,程序仅涉及到前端的开发。
接下来使用 JSON 服务器 作为后端。
使用 npm install -g json-server 执行全局安装 json-server,也可以在应用根目录使用 npx json-server --port 3001 --watch db.json 运行 json-server 服务器。
在项目根目录创建 db.json :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
{
"notes" : [
{
"id" : 1 ,
"content" : "我喜欢 react" ,
"date" : "2020-10-29T15:17:10.098Z" ,
"important" : true
},
{
"id" : 2 ,
"content" : "启动电脑开VS,欢迎来到编程世界。" ,
"date" : "2020-10-29T15:18:26.092Z" ,
"important" : false
},
{
"id" : 3 ,
"content" : "GET 和 POST 是 HTTP 协议中最重要的方法" ,
"date" : "2020-10-29T15:17:10.098Z" ,
"important" : true
}
]
}
为什么使用 3001 端口?是因为前端 React 程序占用了 3000 端口,所以将 json-server 设定为 3001 端口。
可以通过 http://localhost:3001/notes 来访问 db.json 的 notes 数据了。
选用 json-server 作为后端服务器的原因是在开发阶段可以很快速的实现功能。实际项目一般会将数据存在数据库中,如 MySQL MongoDB 等。
The browser as a runtime environment
XHR「XMLHttpRequest」是1999年引入的技术,使用 XHR 对象发出 HTTP 请求。
现代浏览器基本上都支持了 promises 的 fetch 方法,而不是 XHR 使用的事件驱动型,所以现在一般也不用 XHR 方法。
但还是有必要了解一下 XHR 方法如何请求数据的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest ()
xhttp . onreadystatechange = function ()
{
if ( this . readyState == 4 && this . status == 200 )
{
const data = JSON . parse ( this . responseText )
}
}
xhttp . open ( 'GET' , '/data.json' , true )
xhttp . send ()
以上将事件处理程序注册到 xhttp 对象,当 xhttp 的状态发生改变时执行。XHR 请求是异步执行 ,并非自上而下的同步执行。
JavaScript 引擎,或者运行环境,遵循异步模型 。原则上所有的 IO 操作「除了一些特例」都以非阻塞方式执行。这意味着代码执行在调用 IO 函数之后立即继续,而不需要等待它返回。
异步操作完成的某个时刻,JavaScript 引擎才会调用注册到该操作的事件处理程序。
JavaScript 是单线程的,所以它并不能并行执行代码,若没有使用非阻塞方式,浏览器将会在执行代码时卡住,直到代码执行结束才恢复响应。
为了保证浏览器的 responsive,代码逻辑要让任何一个单一计算不花费太多时间。
现代浏览器可以使用 Web Worker 来运行并行化代码。但注意的是单个浏览器窗口仍然是由一个单线程处理。
npm
目前几乎所有 JavaScript 项目都是使用 node 包管理器定义的,也就是 npm。使用 npm 会在项目根目录创建一个 package.json 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
{
"name" : "notes" ,
"version" : "0.1.0" ,
"private" : true ,
"dependencies" : {
"@testing-library/jest-dom" : "^4.2.4" ,
"@testing-library/react" : "^9.4.0" ,
"@testing-library/user-event" : "^7.2.1" ,
"react" : "^16.12.0" ,
"react-dom" : "^16.12.0" ,
"react-scripts" : "3.3.0"
},
"scripts" : {
"start" : "react-scripts start" ,
"build" : "react-scripts build" ,
"test" : "react-scripts test" ,
"eject" : "react-scripts eject"
},
"eslintConfig" : {
"extends" : "react-app"
},
"browserslist" : {
"production" : [
">0.2%" ,
"not dead" ,
"not op_mini all"
],
"development" : [
"last 1 chrome version" ,
"last 1 firefox version" ,
"last 1 safari version"
]
}
}
dependencies 定义了该项目所需要的依赖或外部库。
安装依赖也非常方便,在项目根目录使用终端 npm install axios 命令即可。
当执行完成后,会在 package.json 的 dependencies 中添加 axios。当然我们也可以直接在 package.json 增加这一条,然后在根目录通过执行 npm install 来安装所有依赖 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
}
"dependencies" : {
// ...
"axios" : "^0.19.2" ,
"react" : "^16.12.0" ,
"react-dom" : "^16.12.0" ,
"react-scripts" : "3.3.0"
} ,
// ...
}
如何安装开发依赖?开发依赖是在开发中提供帮助,实际项目并不需要它。
1
npm install json-server --save-dev
以上安装了 JSON 服务器,在 package.json 中增加 server script 来帮助我们快速启动 JSON 服务器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
// ...
"scripts" : {
"start" : "react-scripts start" ,
"build" : "react-scripts build" ,
"test" : "react-scripts test" ,
"eject" : "react-scripts eject" ,
"server" : "json-server -p3001 --watch db.json"
},
}
这样可以通过 npm run server 来启动 JSON 服务器了。
Axios and promises
axios 库是代替浏览器和服务器之间的通信,功能类似于 fetch。在上一节使用 npm 安装了 axios 库,在项目中像引入 react 库一样 import 即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import axios from 'axios'
const promise = axios . get ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' )
console . log ( promise )
const promise2 = axios . get ( 'http://localhost:3001/foobar' )
console . log ( promise2 )
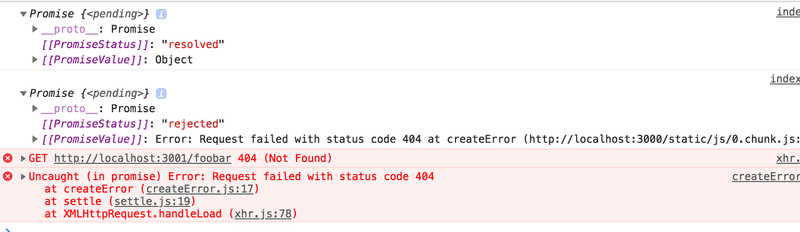
由于 JSON 服务器中仅有 notes 数据,所以访问 http://localhost:3000 控制台会有报错,如下:
Axios 的 get 方法会返回一个 promise 。
Mozilla’s 网站上的文档对 promises 的解释:
A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation.
Promise承诺是一个对象,用来表示异步操作的最终完成或失败。
promise 是一个表示异步操作的对象,有三种不同状态
The promise is pending
The promise is fulfilled
The promise is rejected
pending 表示还在提交中,最终值处于不可用状态。
fulfilled 表示数据已兑现,操作成功,最终值可用。这种状态有时也被称为 resolve。
rejected 表示拒绝,操作失败,说明出现了错误阻止最终值。
回到上面的示例,在一个请求的 PromiseStatus 是 resolved 也就是 fulfilled 状态,表示是成功的。而第二个是 rejected,控制台提示错误原因,是因为我们HTTP GET 请求的地址是不存在的「404错误」。
如果我们想要访问 promise 表示的操作结果,必须要向 promise 注册一个事件处理程序。这里是使用 then 方法实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
const promise = axios . get ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' )
promise . then ( response =>
{
const notes = response . data
})
JavaScript 运行时环境调用由 then 方法注册的回调函数,并提供一个 response 对象作为参数。response 对象包含与 HTTP GET 请求响应相关的所有基本数据,也包括返回的 data、status code 和 headers。
通常情况下,没有必要将 promise 对象存储在一个变量中,而且将 then 链接到 axios 方法中也是很常用的。所以重构代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
axios
. get ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' )
. then ( response =>
{
const notes = response . data
})
服务器返回的数据是纯文本,基本上只有一个长字符串。 Axios 库仍然能够将数据解析为一个 JavaScript 数组,因为服务器使用 content-type 头指定数据格式为 application/json; charset=utf-8。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import App from './App'
import axios from 'axios'
axios . get ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' ). then ( response => {
const notes = response . data
ReactDOM . render (
< App notes = { notes } />,
document . getElementById ( 'root' )
)
})
以上方法向本地服务器请求数据并渲染,虽然也能够执行,但它只有在将整个 App 组件渲染完成后才会得到成功的 response。而且 axios.get 命令应该放在组件中的哪个位置也是个问题。
这样的方法不是很好,在实际开发中会遇到很多问题。
结合 Effect hooks 可以很好的处理。
Effect-hooks
16.8.0版本还引入了 effect hooks 新特性。 像文档里说的:
The Effect Hook lets you perform side effects in function components. Data fetching, setting up a subscription, and manually changing the DOM in React components are all examples of side effects.
Effect Hook 可以让你在函数组件中执行副作用。数据获取、设置订阅和手动更改 React 组件中的 DOM 都是副作用的例子。
因此,effect hooks正是从服务器获取数据时使用的正确工具。
更改原先的代码,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
import React , { useState , useEffect } from 'react'
import axios from 'axios'
import Note from './components/Note'
const App = () =>
{
const [ notes , setNotes ] = useState ([])
const [ newNote , setNewNote ] = useState ( '' )
const [ showAll , setShowAll ] = useState ( true )
useEffect (()=>
{
console . log ( 'effect' )
axios
. get ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' )
. then ( response =>
{
console . log ( 'promise 兑现' )
setNotes ( response . data )
})
}, [])
console . log ( 'render' , notes . length , '笔记' )
// ...
}
执行上述代码后,控制台会依次显示以下内容:
1
2
3
4
render 0 笔记
effect
promise fulfilled
render 3 笔记
useEffect 函数一共有2个参数,第一个是函数本身,根据文档描述:
By default, effects run after every completed render, but you can choose to fire it only when certain values have changed.
默认情况下,effects 在每次渲染完成后运行,但是你可以选择只在某些值发生变化时才调用。
第二个是指定effect运行的频率 。[] 空数组表示只在组件的第一次渲染时运行。
1
useEffect ( function , [])
The development runtime environment
目前为止项目的运行环境情况如下图:
在服务端将数据 Alert 出来
REST 表现层状态转换
REST(Representational state transfer) ,不是一种标准,而是一种设计风格。REST通常基于HTTP、URI、XML以及HTML这些现有的广泛流行的协议和标准。
在 REST 术语中,我们将单个数据对象(如应用中的便笺)称为 resources。 每个资源都有一个唯一的地址——它的 URL。 根据 json-server 使用的一般约定,我们将能够在资源 URL, 即 notes/3 上定位某个便笺,其中3是资源的 id。 另一方面, notes url 指向包含所有便笺的资源集合。
通过 HTTP GET 请求从服务器获取资源。 例如,对 URL notes/3 的 HTTP GET 请求将返回 id 为3的便笺。 对 notes URL 的 HTTP GET 请求将返回所有便笺的列表。
根据 json 服务器遵守的 REST 约定,通过向 notes URL 发出 HTTP POST 请求来创建、存储新的便笺。 新便笺资源的数据在请求的 body 中发送。
Json-server 要求以 JSON 格式发送所有数据。 实际上,这意味着数据必须是格式正确的字符串,并且请求必须包含值为 application/json 的 Content-Type 请求头。
Sending Data to the Server 发送数据到服务器
使用 POST 方法将对象发送至服务器,创建一个新对象,不需要发送 id 属性,因为 id 交给服务器生成更加合理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
addNote = ( event ) =>
{
event . preventDefault ()
const newObject =
{
content : newNote ,
date : new Date (),
important : Math . random () < 0.5 ,
}
axios
. post ( 'http://localhost:3001/notes' , newObject )
. then ( response =>
{
setNotes ( notes . concat ( response . data ))
setNewNote ( '' )
})
}
在 POST 请求中发送的数据是一个 JavaScript 对象,axios 自动懂得为 Content-Type 头设置适当的 application/json 值。
通过 Chrome 开发工具的 Network 选项卡检查 HTTP 请求来查看是否符合预期。
Postman 工具用来调试服务器应用非常易用,Chrome 扩展官方已弃用(DEPRECATED),使用 App 功能更加强大。
Changing the important of Notes
向 Note 组件添加用于调整 Notes 的 important 值的按钮:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
const Note = ({ note , toggleImportance }) =>
{
const label = note . important ? '设置为不重要' : '设置为重要'
return (
< li >
{ note . content }
< button onClick = { toggleImportance }>{ label }</ button >
</ li >
)
}
在 App 组件增加事件处理程序 toggleImportance:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
const App = () =>
{
const [ notes , setNote ] = useState ([])
const [ newNote , setNewNote ] = useState ( '' )
const [ showAll , setShowAll ] = useState ( true )
// ...
const toggleImportance = ( id ) =>
{
const url = `http://localhost:3001/notes/ ${ id } `
const note = notes . find ( note => note . id === id )
const changeNote = { ... note , important : ! note . important }
axios
. put ( url , changeNote )
. then ( response =>
{
setNotes ( notes . map ( note => note . id !== id ? note : response . data ))
})
}
// ...
return (
< div >
< h1 > 笔记 </ h1 >
< div >
< button onClick = {() => setShowAll ( ! showAll )}>
show { showAll ? '显示重要' : '显示全部' }
</ div >
< ul >
{ noteToShow . map (( note ) =>
< Note
key = { note . id }
note = { note }
toggleImportance = {() => toggleImportance ( note . id )}
/>
)}
</ ul >
// ...
</ div >
)
}
通过 PUT 方法把对应 id 的 note 修改,修改成重要或是不重要。并通过回调函数将组件内的 Notes 状态更新。
将与后端通信提取到单独的模块中去,常用的存放目录是 src/services。
在 services 目录下创建 note.js:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
import axios from 'axios'
const baseUrl = 'http://localhost:3001/notes'
const getAll = () => axios . get ( baseUrl )
const create = ( newObject ) => axios . post ( baseUrl , newObject )
const update = ( id , newObject ) => axios . put ( ` ${ baseUrl } / ${ id } ` , newObject )
export default
{
getAll : getAll ,
create : create ,
update : update
}
修改 App.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
// ...
import noteService from './services/notes'
const App = () =>
{
// ...
useEffect (() =>
{
noteService
. getAll ()
. then ( response =>
{
setNotes ( response . data )
})
}, [])
const toggleImportance = ( id ) =>
{
const note = notes . find ( note => note . id === id )
const changeNote = { ... note , important : ! note . important }
noteService
. update ( id , changeNote )
. then ( response =>
{
setNotes ( notes . map ( note => note . id !== id ? note : response . data ))
})
}
const addNote = ( event ) =>
{
event . preventDefault ()
const noteObject = {
content : newNote ,
date : new Date (). toISOString (),
important : Math . random () > 0.5
}
noteService
. create ( noteObject )
. then ( response => {
setNotes ( notes . concat ( response . data ))
setNewNote ( '' )
})
}
// ...
}
export default App
如果整个 App 只使用 response 对象的 response.data 属性,那么可以使用如下方法会更好一些。
services/note.js 做如下修改;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
const getAll () =>
{
const request = axios . get ( baseUrl )
return request . then ( response => response . data )
}
// 其余方法以此类推
相应的 App 组件里对应的 service 也要做修改:
1
2
3
4
5
6
noteService
. getAll ()
. then ( initialNotes =>
{
setNotes ( initialNotes )
})
getAll 函数返回了一个 Promise, 当 HTTP 请求成功时,Promise 将返回从后端响应中发送回来的数据。
承诺Promise是现代 JavaScript 开发的核心,需要投入一定时间理解它们。
You do not know JS - Chapter 3 Promises
Promise chaining
cleaner syntax for defining object literals 用于定义对象字面量的更清晰的语法
上章节中,service/note.js 最后 export 了三个对象:
1
2
3
4
5
6
export default
{
getAll : getAll ,
create : create ,
update : update
}
在对象定义中,冒号左侧的标签是对象的键,而它右侧的标签是在模块内部定义的 variables。
由于键和赋值变量是相同的,同时也因 ES6 引入到 JavaScript 中,可以简化成如下:
1
export default { getAll , create , update }
Promises and errors
使用 catch 方法来处理 Promise 是 reject 的状态的情况。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
axios
. get ( 'http://localhost:3001/foobar' )
. then ( response =>
{
console . log ( '请求成功' )
})
. catch ( error =>
{
console . log ( '请求失败' )
})
通常 catch 方法置于 Promise 链 的更深处来使用,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
axios
. get ( baseUrl )
. then ( response => response . data )
. then ( changeNote =>
{
// ...
})
. cartch ( error => console . log ( '请求失败' )
修改原先 App 组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
const toggleImportanceOf = id => {
const note = notes . find ( n => n . id === id )
const changedNote = { ... note , important : ! note . important }
noteService
. update ( id , changedNote ). then ( returnedNote => {
setNotes ( notes . map ( note => note . id !== id ? note : returnedNote ))
})
. catch ( error => {
alert (
`未找到该条 ' ${ note . content } ' 笔记,可能已从服务器删除。`
)
setNotes ( notes . filter ( n => n . id !== id ))
})
}
给 React 应用加点样式
导入外部 css 文件的方式,在 index.js 使用 import
之后在 index.css 添加相关样式即可。常规 html 文件在元素中使用 class 属性来对应样式表的类选择器,而 react 中需要使用 className 来对应。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const Note = ({ note , toggleImportance }) => {
const label = note . important
? '设置为不重要'
: '设置为重要' ;
return (
< li className = 'note' >
{ note . content }
< button onClick = { toggleImportance }>{ label }</ button >
</ li >
)
}
内联样式的使用方法如下:
需要注意的是,内联样式中无法使用 伪类 pseudo-classes 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
const Footer = () => {
const footerStyle = {
color : 'green' ,
fontStyle : 'italic' ,
fontSize : 16
}
return (
< div style = { footerStyle }>
< br />
< em > footer content </ em >
</ div >
)
}
内联样式和其他一些将样式添加到 React 组件的方法完全违背了旧的惯例。 传统上,将 CSS 与内容(HTML)和功能(JavaScript)解耦被认为是最佳实践。 根据这个古老的思想流派,我们的目标是将 CSS、 HTML 和 JavaScript 编写到它们各自的文件中。
React的哲学,事实上,是这个极端的对立面。 由于将 CSS、 HTML 和 JavaScript 分离成单独的文件在大型应用中似乎不利于伸缩,所以 React 将应用按照其逻辑功能实体进行划分。
构成应用功能实体的结构单元是 React 组件。 React 组件定义了组织内容的 HTML,确定功能的 JavaScript 函数,以及组件的样式; 所有这些都放在一个地方。 这是为了创建尽可能独立和可重用的单个组件。